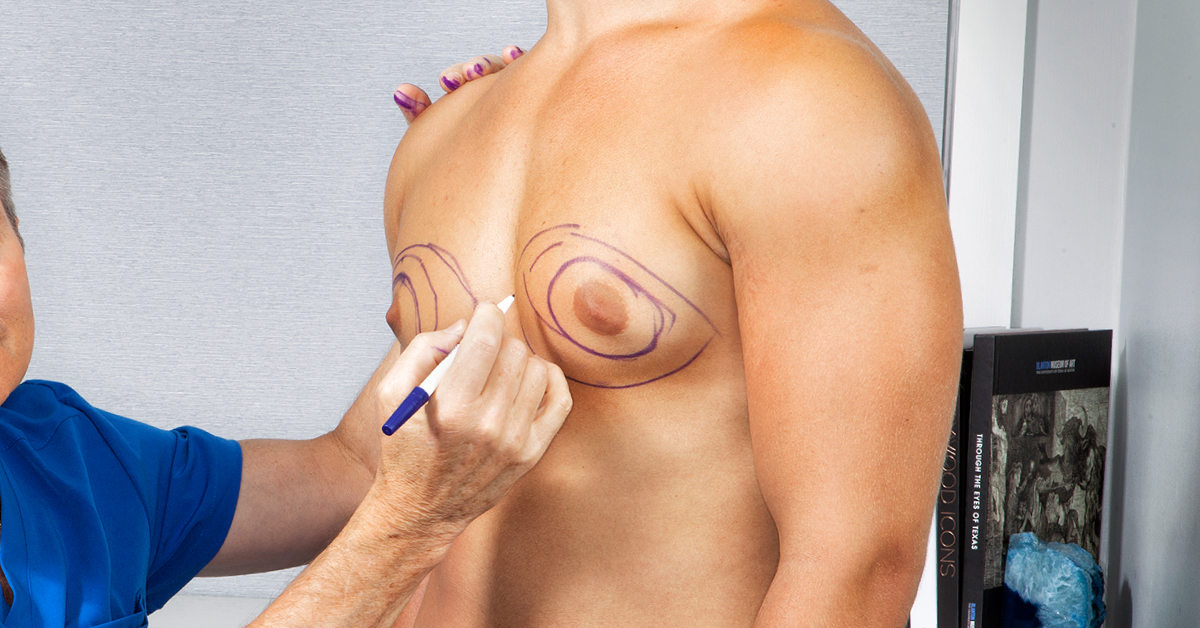
Understanding the difference between gynecomastia and chest fat is crucial for men who notice changes in their chest’s appearance. While both conditions may result in a similar look, their underlying causes and treatments are vastly different. Gynecomastia refers to the abnormal enlargement of glandular breast tissue caused by hormonal imbalances, whereas chest fat, or pseudogynecomastia, is simply the result of excess fatty deposits. Recognizing these distinctions is the first step toward identifying the appropriate course of action and regaining confidence in your body.
This article explores the key differences between gynecomastia and chest fat, focusing on their symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Whether the issue stems from hormonal shifts or lifestyle factors, understanding these two distinct conditions can help you take the right steps toward achieving your desired chest appearance.
What Is Gynecomastia?
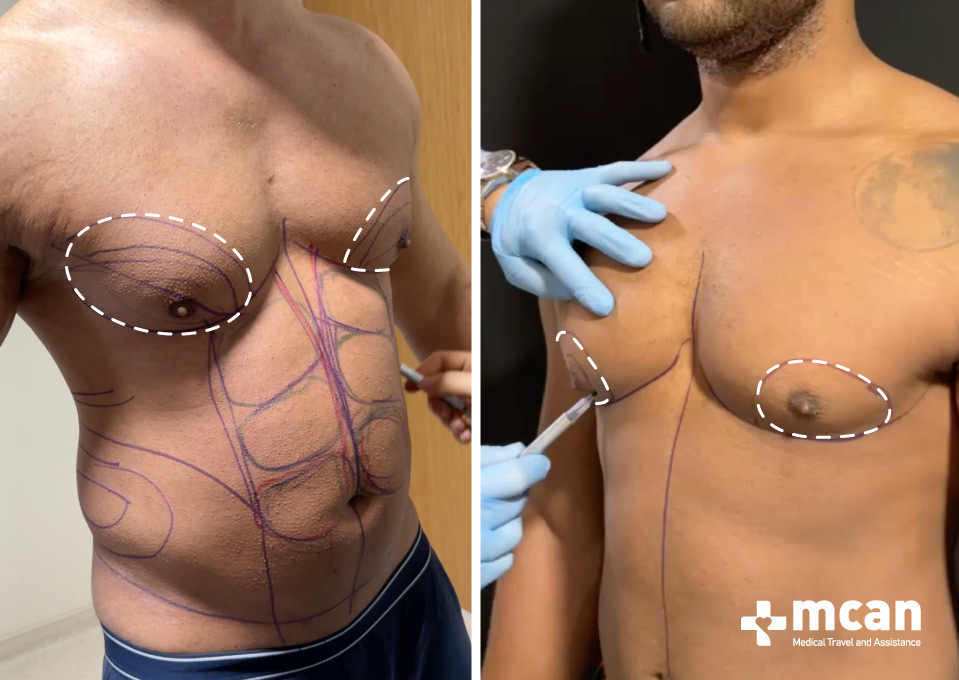
Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement of breast tissue in males. This occurs due to an imbalance between estrogen, which stimulates breast tissue growth, and testosterone, which inhibits it. Unlike general chest fat caused by weight gain, gynecomastia involves the growth of glandular tissue and is often firm to the touch. It can affect one or both breasts and may occur symmetrically or asymmetrically.
Although gynecomastia often resolves on its own, persistent cases may require medical intervention to address physical and emotional discomfort.
Signs and Symptoms of Gynecomastia
Recognizing the distinct features of gynecomastia is essential for determining the underlying cause and choosing the right approach to address it.
Below are the most common signs of gynecomastia to differentiate from other chest-related concerns:
- Enlarged Breast Tissue
Gynecomastia presents as a noticeable swelling of the breast area, typically centered under the nipple. This growth involves glandular rather than fatty tissue, giving it a firm texture. - Nipple Sensitivity
Affected individuals may experience tenderness or sensitivity around the nipple and areola. This discomfort can increase with physical activity or pressure. - Symmetry or Asymmetry
Enlargement may occur in one breast (unilateral) or both breasts (bilateral), sometimes leading to visible asymmetry. - Rubbery or Firm Mass
A distinct, rubbery mass can often be felt beneath the nipple, distinguishing gynecomastia from fatty deposits in the chest. - Potential Skin Changes
In some cases, mild skin tightness or stretching may accompany tissue enlargement.

What Is Chest Fat?
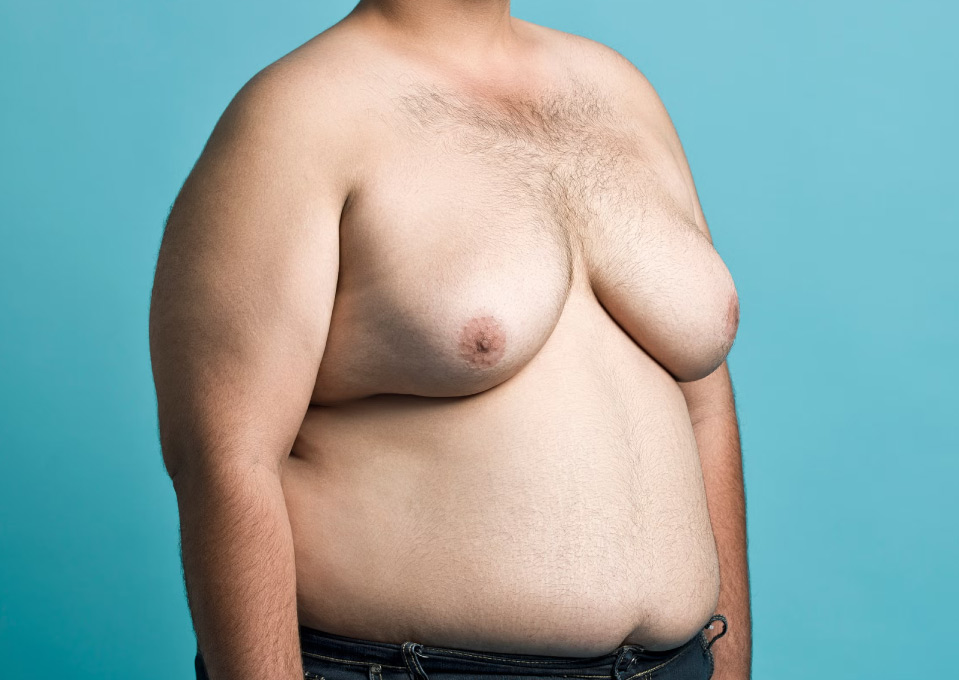
Chest fat, medically referred to as pseudogynecomastia, is the accumulation of fatty tissue in the chest area, often caused by excess weight or obesity. Unlike gynecomastia, which involves the enlargement of glandular tissue, chest fat is solely composed of adipose tissue. This condition is typically related to overall body fat distribution and is not linked to hormonal imbalances.
Chest fat can occur in individuals of any age and is most commonly observed in men who have a higher body mass index (BMI). While not a medical concern, chest fat can impact self-confidence and physical appearance, leading some individuals to seek lifestyle changes or cosmetic procedures to reduce its prominence.
Signs and Symptoms of Chest Fat
Identifying the characteristics of chest fat can help you better understand the changes in your chest’s appearance and determine whether lifestyle adjustments or other actions are needed.
Below are the key signs of chest fat:
- Soft and Uniform Texture
Chest fat feels soft and consistent to the touch, without the firm or rubbery texture associated with gynecomastia. - Symmetrical Appearance
Fat deposits typically appear evenly distributed across both sides of the chest, though variations may occur depending on overall fat distribution. - Lack of Nipple Sensitivity
Unlike gynecomastia, chest fat is not usually accompanied by tenderness, sensitivity, or pain around the nipple area. - Change with Weight Fluctuations
The size and appearance of chest fat often increase with weight gain and may decrease with weight loss or targeted exercise. - Absence of Underlying Mass
No distinct mass or lump is felt beneath the nipple, distinguishing chest fat from glandular enlargement seen in gynecomastia.
Causes of Gynecomastia vs. Chest Fat
Understanding the root causes of gynecomastia and chest fat is crucial for identifying the appropriate treatment options. Below is an expanded comparison, detailing the contributing factors to each condition for better differentiation:
| Cause | Gynecomastia | Chest Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Imbalance | Caused by elevated estrogen or reduced testosterone levels. Triggered by puberty, aging, or conditions like hypogonadism or hyperthyroidism. | Not caused by hormonal imbalance directly. Obesity-related hormonal shifts may slightly influence estrogen levels. |
| Obesity and Lifestyle | Obesity does not directly cause gynecomastia but can worsen its appearance. Fat tissue produces aromatase, converting testosterone into estrogen. | Caused by excess fat accumulation due to poor diet, inactivity, or sedentary habits. Unrelated to hormonal imbalances. |
| Medical Conditions | Triggered by liver/kidney disease, thyroid disorders, or testicular/adrenal tumors, which disrupt hormone production. | Not directly caused by medical conditions but linked to obesity-related disorders like metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes. |
| Medications | Caused by drugs like anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, antidepressants, antipsychotics, or cancer treatments that disrupt hormones. | Not directly caused by medications, but drugs like corticosteroids or certain antidepressants may contribute to weight gain. |
| Age and Life Stages | Common during puberty and older age due to natural hormonal fluctuations, such as testosterone decline or temporary imbalances. | Can occur at any age but is more frequent in individuals with long-term weight gain or poor physical fitness. |
| Genetics | Genetic conditions, such as Klinefelter syndrome, can predispose individuals to gynecomastia by altering hormone production. | Family history of obesity or a predisposition to storing fat in the chest area can increase the likelihood of chest fat. |
| Diet and Nutrition | Diets rich in phytoestrogens (e.g., soy products) or certain herbal supplements might contribute to hormonal imbalances. | High-calorie diets or frequent consumption of processed, fatty foods directly lead to fat accumulation in the chest. |
| Physical Activity Levels | Lack of exercise can worsen gynecomastia symptoms by contributing to fat accumulation, which highlights glandular tissue enlargement. | A sedentary lifestyle directly contributes to fat buildup, making the chest appear larger due to increased adipose tissue. |
Ways to Diagnose the Difference
Distinguishing between gynecomastia and chest fat can be challenging without proper evaluation. Both conditions may look similar but have distinct characteristics.
Here are the most effective ways to identify the difference:
Visual Assessment: Symmetry & Shape
Gynecomastia:
Gynecomastia often appears as a rounded or conical enlargement directly beneath the nipple, giving the chest a more pointed appearance. It may be asymmetrical, with one side larger than the other.
Chest Fat:
Chest fat tends to have a broader, softer appearance, spreading evenly across the chest area. It is typically symmetrical, aligning with general fat distribution across the body.
Tenderness or Sensitivity
Gynecomastia:
Tenderness is a hallmark symptom of gynecomastia. The area around the nipple and areola may feel sore or sensitive to touch due to the growth of glandular tissue and hormonal activity.
Chest Fat:
Chest fat does not usually cause tenderness or pain. The fatty tissue feels soft and is painless even when pressed.
Hormonal Triggers and Clues
Gynecomastia:
Gynecomastia often accompanies conditions or phases involving hormonal changes, such as puberty, aging, or medical conditions affecting hormone levels. Men may notice other signs of hormonal imbalance, such as reduced libido or muscle mass.
Chest Fat:
Chest fat is linked to overall body weight and lifestyle rather than hormonal changes. It is more common in individuals with higher body fat percentages and does not present signs of hormonal disruption.
Age and Life Stage
Gynecomastia:
Gynecomastia frequently appears during life stages involving hormonal fluctuations, such as adolescence or older adulthood. For teenagers, it may be temporary, whereas in older men, it often persists due to declining testosterone levels.
Chest Fat:
Chest fat can occur at any age and is primarily tied to weight gain. It is not restricted to specific hormonal changes in life stages.
Professional Diagnosis
A medical evaluation is often the most reliable way to distinguish between gynecomastia and chest fat. A healthcare professional may use the following tools:
- Medical History: Questions about onset, duration, medications, and associated symptoms.
- Physical Examination: Identifying the texture, size, and location of the chest enlargement.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasounds or mammograms can confirm the presence of glandular tissue in gynecomastia.
To gain a deeper understanding of the progression of gynecomastia, you can check to our detailed article: In Which Stages of Gyno Are You?
The Gynecomastia Pinch Test
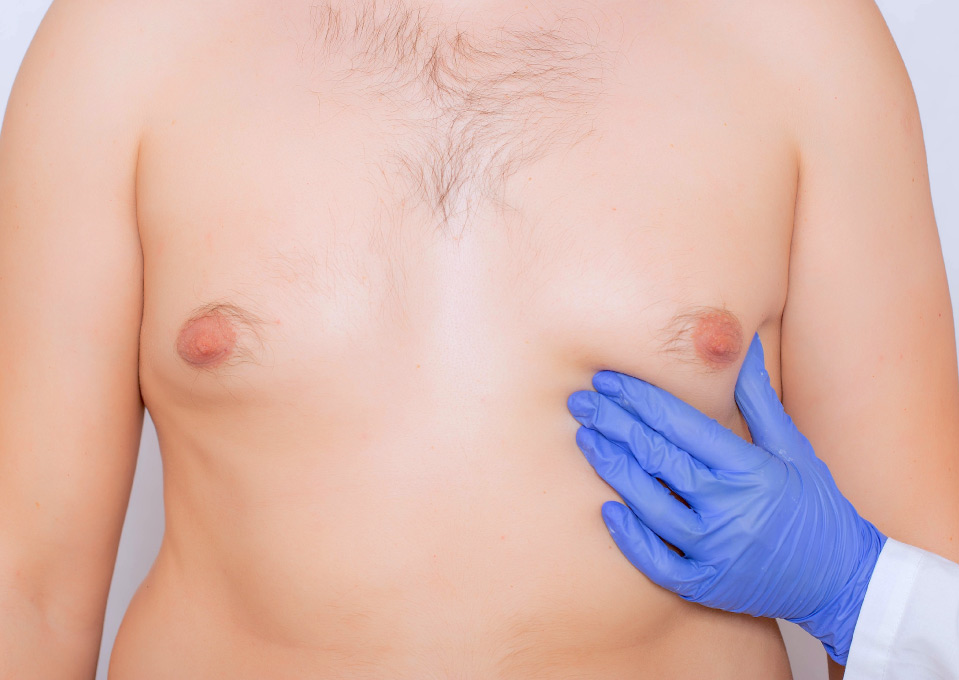
The Gynecomastia pinch test is a simple yet effective method to differentiate between gynecomastia and chest fat:
- Gynecomastia: Gently pinch the area directly beneath your nipple. If you feel a firm, rubbery lump or disk, that’s likely glandular tissue a clear sign of gynecomastia. This tissue is denser and doesn’t feel like typical fat.
- Chest Fat: Pinching the same area will reveal a soft, even texture if it’s chest fat. There’s no hard lump or disk beneath the nipple, as the tissue is made up entirely of fat.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to determine the right course of treatment. If there is uncertainty, seeking a professional evaluation ensures the condition is correctly identified and managed.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia & Chest Fat
Managing gynecomastia and chest fat requires tailored approaches depending on the underlying cause. While gynecomastia often necessitates medical or surgical intervention, chest fat can typically be addressed through lifestyle changes.
Gynecomastia Treatment
- Observation and Monitoring: In adolescent cases, gynecomastia often resolves naturally as hormone levels stabilize. Regular monitoring may be recommended if the condition is mild and not causing discomfort.
- Medical Treatments: Hormonal therapies, such as testosterone replacement or anti-estrogen medications, may help balance hormone levels in persistent cases. These treatments are most effective when the hormonal imbalance is clearly identified.
- Surgical Options:
- Liposuction: Effective for removing excess fatty tissue in gynecomastia.
- Excision Surgery: Performed to remove glandular tissue and excess skin, particularly in more severe cases.
- Combination Approach: A blend of liposuction and excision for optimal chest contouring.
- Post-Surgery Care: After surgery, wearing a compression garment and following aftercare instructions helps ensure proper healing and the best results.
Chest Fat Reduction
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Diet: Adopting a balanced diet with a calorie deficit can help reduce overall body fat, including chest fat. Focus on lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, including cardio and strength training, specifically targeting the chest muscles, can tone and reduce chest fat. Exercises like push-ups, bench presses, and dumbbell flys are particularly effective.
- Medical or Cosmetic Procedures:
For individuals struggling with stubborn chest fat despite weight loss, procedures like liposuction can help remove excess fat and sculpt the chest area. - Consistency is Key:
Sustained effort through healthy habits is essential for reducing chest fat and preventing its recurrence.
Why Choose MCAN Health for Gynecomastia Surgery in Turkey?
Addressing gynecomastia requires specialized care to ensure effective and lasting results. At MCAN Health, we are dedicated to providing tailored treatments that restore confidence and improve quality of life.
If you’re facing gynecomastia, not chest fat, MCAN Health is your ultimate destination for expert treatment and lasting results for your gynecomastia surgery in Turkey.
Here’s why men from around the world trust us:
World-Renowned Surgeons
Our surgeons are members of ASPS (American Society of Plastic Surgeons) and EBOPRAS (European Board of Plastic, Reconstructive, and Aesthetic Surgery), ensuring international expertise. Each surgeon is carefully selected based on MCAN Health’s rigorous criteria, including performance metrics, patient satisfaction, and surgical excellence.
Accredited State-of-the-Art Facilities
Your treatment is performed in internationally accredited hospitals equipped with cutting-edge technology and adhering to the highest safety standards.
Comprehensive All-Inclusive Packages
From luxury hotel accommodations and airport transfers to multilingual patient hosts and post-op care, MCAN Health ensures a seamless, stress-free experience.
Affordable, Transparent Pricing
Receive world-class gynecomastia treatment at a fraction of the cost compared to other countries, with no hidden fees or surprises.
Dedicated Post-Surgical Support
Our in-house English speaking nurses provide daily hotel visits for dressing changes, vital checks, and personalized recovery guidance. A 24/7 support team is available for any concerns.
Trusted Expertise
With over 15,000 satisfied patients and a 4.8-star rating, MCAN Health is a leader in plastic surgery treatments, known for delivering confidence-restoring results.

 Understanding The Different Types Of Alopecia
Understanding The Different Types Of Alopecia  Foreign Office Officials Issue Warning Over British People Traveling to Turkey for Medical Treatment
Foreign Office Officials Issue Warning Over British People Traveling to Turkey for Medical Treatment  Can You Wear a Hat After Hair Transplant?
Can You Wear a Hat After Hair Transplant?